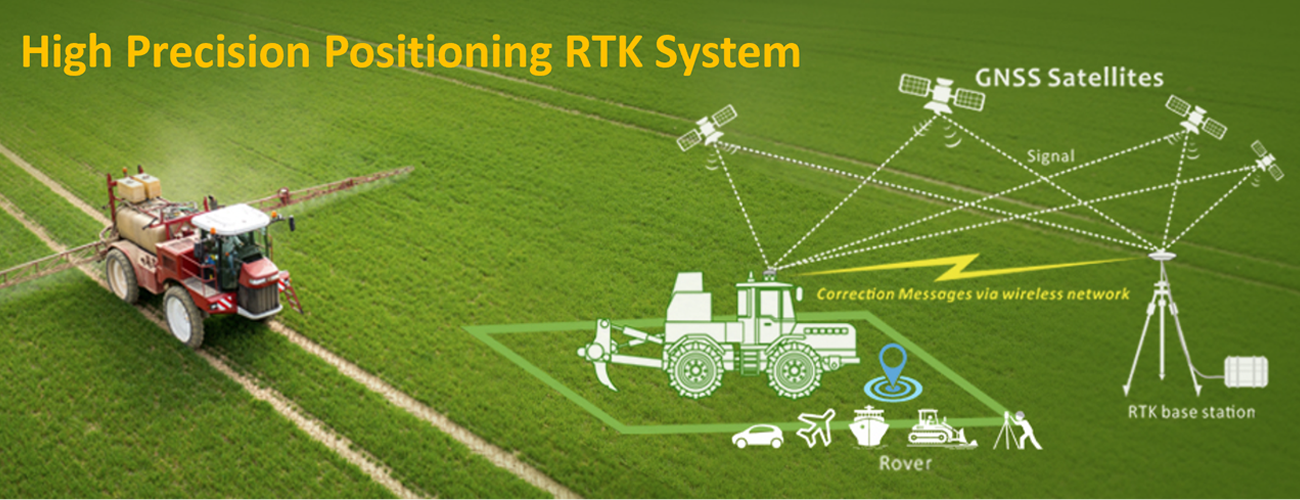
A high-precision GNSS antenna is designed to receive signals from multiple satellite constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo, to provide accurate positioning and navigation. These antennas are engineered to minimize signal interference and multipath errors, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications such as surveying, autonomous vehicles, and geophysical research.
Key characteristics of high-precision GNSS antennas include:
- Multi-frequency support – They operate on multiple GNSS bands (e.g., L1, L2, L5) to enhance accuracy and reduce signal errors.
- Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP) – This helps capture satellite signals effectively while reducing interference.
- Low-noise amplification – Active GNSS antennas include built-in amplifiers to boost weak signals before they reach the receiver.
- Stable phase center – Ensures consistent signal reception, which is crucial for precision applications.